Introduction
How to Setup FTP Server with VSFTPD on Ubuntu 18.04
FTP, short for File Transfer Protocol, is a network protocol that was once widely used for moving files between a client and server.
It has since been replaced by faster, more secure, and more convenient ways of delivering files. Many casual Internet users expect to download directly from their web browser with https, and command-line users are more likely to use secure protocols such as the scp or sFTP.
FTP is still used to support legacy applications and workflows with very specific needs. If you have a choice of what protocol to use, consider exploring the more modern options. When you do need FTP, however, vsftpd is an excellent choice.
Optimized for security, performance, and stability, vsftpd offers strong protection against many security problems
found in other FTP servers and is the default for many Linux distributions.
In this tutorial, we’ll show you how to configure vsftpd
to allow a user to upload files to his or her home directory using FTP with login credentials secured
by SSL/TLS.
Prerequisites
Before continuing with this tutorial, make sure you are logged in as a user with sudo privileges.
How to Setup FTP Server with VSFTPD on Ubuntu 18.04
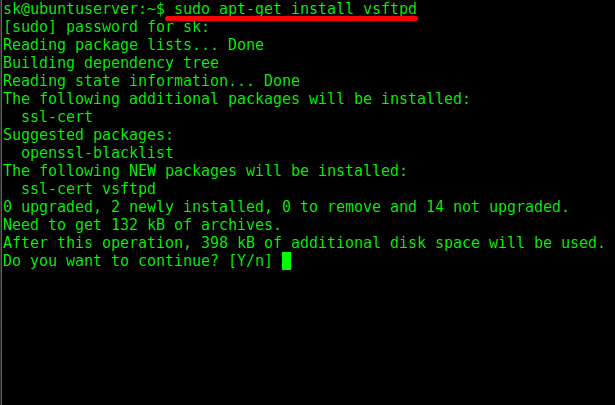
Installing vsftpd on Ubuntu 18.04
The vsftpd package is available in the Ubuntu repositories. To install it, simply run the following commands:
$ sudo apt update $ sudo apt install vsftpd

vsftpd service will automatically start after the installation process is complete. Verify it by printing the service status
$ sudo systemctl status vsftpd
The output will look something like below, showing that the vsftpd service is active and running:

Sample output:
* vsftpd.service - vsftpd FTP server
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/vsftpd.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Mon 2018-10-15 03:38:52 PDT; 10min ago
Main PID: 2616 (vsftpd)
Tasks: 1 (limit: 2319)
CGroup: /system.slice/vsftpd.service
`-2616 /usr/sbin/vsftpd /etc/vsftpd.conf
Configuring vsftpd
The vsftpd server can be configured by editing the /etc/vsftpd.conf file. Most of the settings are well documented inside the configuration file. For all available options visit the official vsftpd page.
In the following sections, we will go over some important settings needed to configure a secure vsftpd installation.
Start by opening the vsftpd configuration file:
$ sudo nano /etc/vsftpd.conf
1. FTP Access
We’ll allow access to the FTP server only the local users, find the anonymous_enable and local_enable directives and verify your configuration match to lines below:
/etc/vsftpd.conf
anonymous_enable=NO local_enable=YES
2. Enabling uploads
Uncomment the write_enable setting to allow changes to the filesystem such as uploading and deleting files
/etc/vsftpd.conf
write_enable=YES
3. Chroot
To prevent the FTP users to access any files outside of their home directories uncomment the chroot setting.
chroot_local_user=YES
By default to prevent a security vulnerability, when chroot is enabled vsftpd will refuse to upload files if the directory that users are locked in is writable.
Use one of the methods below to allow uploads when chroot is enabled.
- Method 1. – The recommended method to allow upload is to keep chroot enabled, and configure FTP directories. In this tutorial, we will create an
ftpdirectory inside the user home which will serve as the chroot and a writableuploadsdirectory for uploading files.
user_sub_token=$USER local_root=/home/$USER/ftp
- Method 2. – Another option is to add the following directive in the vsftpd configuration file. Use this option if you must to grant writable access to your user to its home directory.
allow_writeable_chroot=YES
4. Passive FTP Connections
vsftpd can use any port for passive FTP connections. We’ll specify the minimum and maximum range of ports and later open the range in our firewall
Add the following lines to the configuration file:
pasv_min_port=30000 pasv_max_port=31000
5. Limiting User Login
To allow only certain users to log in to the FTP server add the following lines at the end of the file:
userlist_enable=YES userlist_file=/etc/vsftpd.user_list userlist_deny=NO
When this option is enabled you need to explicitly specify which users are able to log in by adding the user names to the /etc/vsftpd.user_list file (one user per line).
6. Securing Transmissions with SSL/TLS
In order to encrypt the FTP transmissions with SSL/TLS, you’ll need to have an SSL certificate and configure the FTP server to use it.
You can use an existing SSL certificate signed by a trusted Certificate Authority or create a self-signed certificate.
If you have a domain or subdomain pointing to the FTP server’s IP address you can easily generate a free Let’s Encrypt SSL certificate.
We will generate a self-signed SSL certificate using the openssl command.
The following command will create a 2048-bit private key and self signed certificate valid for 10 years. Both the private key and the certificate will be saved in a same file:
$ sudo openssl req -x509 -nodes -days 3650 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout /etc/ssl/private/vsftpd.pem -out /etc/ssl/private/vsftpd.pem
Once the SSL certificate is created open the vsftpd configuration file:
$ sudo nano /etc/vsftpd.conf
Find the rsa_cert_file and rsa_private_key_file directives, change their values to the pam file path and set the ssl_enable directive to YES:
/etc/vsftpd.conf
rsa_cert_file=/etc/ssl/private/vsftpd.pem rsa_private_key_file=/etc/ssl/private/vsftpd.pem ssl_enable=YES
If not specified otherwise, the FTP server will use only TLS to make secure connections.
Restart the vsftpd Service
Once you are done editing, the vsftpd configuration file (excluding comments) should look something like this:
/etc/vsftpd.conf
listen=NO listen_ipv6=YES anonymous_enable=NO local_enable=YES write_enable=YES dirmessage_enable=YES use_localtime=YES xferlog_enable=YES connect_from_port_20=YES chroot_local_user=YES secure_chroot_dir=/var/run/vsftpd/empty pam_service_name=vsftpd rsa_cert_file=/etc/ssl/private/vsftpd.pem rsa_private_key_file=/etc/ssl/private/vsftpd.pem ssl_enable=YES user_sub_token=$USER local_root=/home/$USER/ftp pasv_min_port=30000 pasv_max_port=31000 userlist_enable=YES userlist_file=/etc/vsftpd.user_list userlist_deny=NO
Save the file and restart the vsftpd service for changes to take effect:
$ sudo systemctl restart vsftpd
Opening the Firewall
If you are running an UFW firewall you’ll need to allow FTP traffic.
To open port 21 (FTP command port), port 20 (FTP data port) and 30000-31000 (Passive ports range), run the following commands:
$ sudo ufw allow 20:21/tcp $ sudo ufw allow 30000:31000/tcp
To avoid being locked out, open the port 22:
$ sudo ufw allow OpenSSH
Reload the UFW rules by disabling and re-enabling UFW:
$ sudo ufw disable $ sudo ufw enable
To verify the changes run:
$ sudo ufw status
output
Status: active To Action From -- ------ ---- 20:21/tcp ALLOW Anywhere 30000:31000/tcp ALLOW Anywhere OpenSSH ALLOW Anywhere 20:21/tcp (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6) 30000:31000/tcp (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6) OpenSSH (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)
Creating FTP User
To test our FTP server we will create a new user.
- If you already have a user which you want to grant FTP access skip the 1st step.
- If you set
allow_writeable_chroot=YESin your configuration file skip the 3rd step.
1.Create a new user named newftpuser:
$ sudo adduser newftpuser

2.Add the user to the allowed FTP users list:
$ echo "newftpuser" | sudo tee -a /etc/vsftpd.user_list
3. Create the FTP directory tree and set the correct permissions:
$ sudo mkdir -p /home/newftpuser/ftp/upload $ sudo chmod 550 /home/newftpuser/ftp $sudo chmod 750 /home/newftpuser/ftp/upload $sudo chown -R newftpuser: /home/newftpuser/ftp
As discussed in the previous section the user will be able to upload its files to the ftp/upload directory.
At this point, your FTP server is fully functional and you should be able to connect to your server using any FTP client that can be configured to use TLS encryption such as FileZilla.
Disabling Shell Access
By default, when creating a user, if not explicitly specified the user will have SSH access to the server.
To disable shell access, we will create a new shell which will simply print a message telling the user that their account is limited to FTP access only.
Create the /bin/ftponly shell and make it executable:
$ echo -e '#!/bin/shnecho "This account is limited to FTP access only."' | sudo tee -a /bin/ftponly $ sudo chmod a+x /bin/ftponly
Append the new shell to the list of valid shells in the /etc/shells file:
$ echo "/bin/ftponly" | sudo tee -a /etc/shells
Change the user shell to /bin/ftponly:
$ sudo usermod newftpuser -s /bin/ftponly
Use the same command to change the shell of all users you want to give only FTP access.
Testing FTP Access
We’ve configured the server to allow only the user sammy to connect via FTP. Let’s make sure that’s the case.
Anonymous users should fail to connect: We disabled anonymous access. Here we’ll test that by trying to connect anonymously. If we’ve done it properly, anonymous users should be denied permission:
$ ftp -p 203.0.113.0
output
Connected to 203.0.113.0. 220 (vsFTPd 3.0.3) Name (203.0.113.0:default): anonymous 530 Permission denied. ftp: Login failed. ftp>
or
open your web browser and type the URL ftp://IP, you will be asked to enter username and password to access FTP. Enter your vsftp username and password, then click on the Ok button. You should see the following page:
Conclusion
How to Setup FTP Server with VSFTPD on Ubuntu 18.04
In this tutorial we covered setting up FTP for users with a local account. If you need to use an external authentication source, you might want to look into vsftpd’s support of virtual users. This offers a rich set of options through the use of PAM, the Pluggable Authentication Modules, and is a good choice if you manage users in another system such as LDAP or Kerberos.
The post How to Setup FTP Server with VSFTPD on Ubuntu 18.04 appeared first on Error Hat.
Discover more from Ubuntu-Server.com
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.