In all Linux distributions, such as Ubuntu, the system consists of multiple repositories and PPA. These repositories and PPAs contain different packages/files and the information about the installed software and tools on the system. Finding the list of all those installed repositories and PPAs won’t be possible without a terminal command.
If you want to list the installed PPAs and repositories on the Ubuntu system, you should follow this guide.
However, before moving towards getting the list of repositories and PPAs, it’s better to know about repositories and PPAs.
What are Repositories and PPAs in Ubuntu
All Ubuntu distributions have four kinds of repositories which are:
- Restricted: The ones that are only accessible for device driver.
- Universe: Open-source software that are available for anyone and are free.
- Main: Open-source software which are supported by canonical.
- Multiverse: The restricted software which has copyrights.
PPAs (Personal Package archive) are a special kind of repository, by using PPAs, the software/tools which are not present in the official repository of Ubuntu can also be installed. PPA’s are beneficial when a new version of a certain software/package is installed and that version is not immediately available in the official repository then to install that latest package, PPA can be used.
How to List all the Installed PPAs and Repositories in Ubuntu
To get the list of all installed repositories and PPAs on Ubuntu, there are multiple commands which can be used:
Command 1
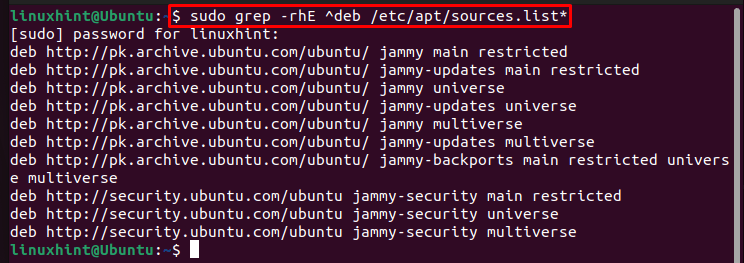
The first command to display the list of installed repositories and PPA’s in Ubuntu is by using the grep command that displays the sources.list file, which contains the installed repositories and PPAs on the Ubuntu system.
By using this command, a complete list of installed repositories and PPAs in your Ubuntu system will appear on the terminal:

Command 2
The other command on our list is the apt-cache command, this command is better as it displays more information about the installed repositories:
In the output, you can see that the list of installed repositories is displayed with the detailed information about each repository.

Command 3
This command is very similar to the previous command, just a little shorter, run the simple apt policy command to display the list of installed repositories and PPAs on Ubuntu:

Get a List of all Installed Repositories and PPAs on Ubuntu Through GUI
The Ubuntu users can also check the list of installed repositories and PPAs on the Ubuntu system through “Software and Update” tool that can be open from the Application Menu.

However, through GUI, you won’t be able to view a detailed list of all installed Repositories and PPAs on the Ubuntu system.

Conclusion
There are three useful terminal commands to get the list of installed repositories and PPAs on Ubuntu. All these commands are helpful to get a detailed list of installed repositories and PPAs. There is also a GUI-based method called “Software & Update” tool, which can be opened from the Application menu to get the list of installed repositories and PPAs on Ubuntu. However, this method fails to provide detailed information of install repositories and PPAs compared to terminal commands.