Ubuntu is an open-source, multi-user, and popular operating system. Ubuntu comes with different pre-installed applications or software that assist users to perform different tasks/operations. However, sometimes users require downloading any additional software applications from the Internet. In such cases, usually, users download Applications through the Official Website or Repository but in some cases, the applications are downloaded from third-party websites. These applications downloaded from third-party or unofficial websites may create a risk to the overall security of the system. Due to this reason, the applications or software downloaded must be verified for their integrity and authenticity.
This article provides a clear explanation of the different verification methods for verifying the Ubuntu ISO File.
Prerequisites
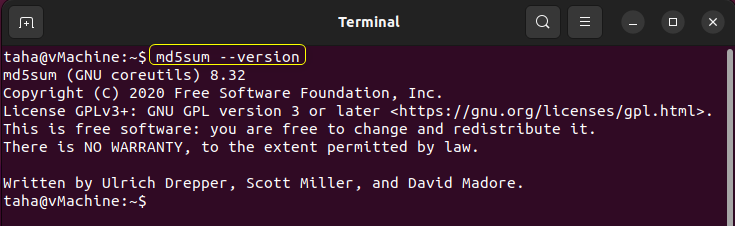
Before Verifying the Integrity of the Downloaded Ubuntu ISO File, Check the md5sum and sha256sum versions on your Ubuntu System. To verify the version of md5sum, use the “–version” command:
The md5sum version will be returned in the Terminal. In our case, it is Version 8.32:
Now, to verify the sha256sum Version, use the “–version” command again:
The sha256sum version will be returned to the Terminal. In our case, it is Version 8.32:
How to Verify Your Ubuntu Download?
The Downloaded Ubuntu ISO File can be verified through the sha256sum checksum command. The sha256sum command checks the file’s integrity. If a slight change is made in the file, the sha256 hash value generated will be completely different from the official Ubuntu ISO File Hash value. The sha256 Hash Value can be verified from the Official Ubuntu Website.
Download Ubuntu Desktop
Before Verifying the Ubuntu ISO Image File, you have to Download it from the Official Ubuntu Website. To Download the Ubuntu ISO File, open your favorite browser and search for Ubuntu Download through the URL. The Official Ubuntu Website link will appear. Click on it to access the Official page of Ubuntu Download:
Instead of searching for the Ubuntu ISO File through the URL or any search engine, visit the Download Ubuntu official Website to access the page directly:
In the Ubuntu Official Download Page, scroll down and look for the latest Ubuntu LTS Version. The newest version available is the Ubuntu 22.04.3 LTS. Click on the “Download 22.04.3” Button to start Downloading the Ubuntu ISO File:
The Ubuntu ISO File will start downloading. Wait for the Download to complete:
Now, once the Download Completes, you can verify the Ubuntu Download by Comparing the “sha256sum” Hash Value. The “sha256sum” Hash Value can be verified using the following Methods:
- Verify the Ubuntu Download Using the Official Ubuntu Checksum.
- Verify the Ubuntu Download with the “Digests” Method.
- Verify the Ubuntu Download with the “sha256sum” Command.
- Verify the Ubuntu Download by Comparing the SHA256SUM and SHA256SUM.gpg Files.
Each Method is clearly demonstrated below.
Method 1: Verify Ubuntu ISO Using the Official Ubuntu Verification Command
After you click on the “Download” button, you will be redirected to a new page. On the page, you will see the “verify your download” link. Click on the “verify your download” Link:
A Pop-up will appear and it will display a message box with an Ubuntu Command:
Now, navigate to the file directory where Ubuntu was downloaded. In our case, it was downloaded in the Ubuntu Directory inside the Downloads Directory:
Open the Directory Path in the Terminal:
Open the Ubuntu Web Page again and copy the “echo” command by selecting the Command and then right-clicking on the selected command:
Paste the Command in the Terminal:
Press enter and wait for the Terminal to verify the Download. The cursor blinking at the next line ensures that the verification process is still proceeding:
If the Terminal Outputs the below message, it means the Ubuntu File is verified:
In our case, the Terminal outputs the same message confirming the integrity and authenticity of the file:
Method 2: Verify Ubuntu ISO Using the “Digests” Method
The Ubuntu ISO File can also be verified through the “Digests” method where you generate the Hash Value through the Digest Property of the File. The Digest Method generates and verifies the digital signature of a File. Before using the Digest Method, you have to install the “gtkhash” utility that will compute the Digest or checksum. Install the “gtkhash” utility in Ubuntu with the “apt” command as follows:
This will download and install the “nautilus-gtkhash” packages and set it up:
Once the “gtkhask” utility downloads, restart Nautilus. Nautilus is an Ubuntu File Manager that can manage our Files. Apart from restarting Nautilus, enable Digests in the Properties of the file by quitting the “nautilus” desktop file manager with the following command:
This will exit any running file managers, and will restart Nautilus:
Now, navigate to the Downloaded Ubuntu ISO File directory. In our case, the Ubuntu ISO File is located in the Ubuntu Directory inside the Downloads Directory:
Right-click on the ISO File. The File Options will appear and select the “Properties” option:
The Properties Dialogue Box will appear, click on the “Digests” Option to Open the Digest Menu:
The Digest Menu will appear where all the Hash Functions will be listed:
As we have to verify the Ubuntu ISO File using the SHA256 checksum, click on the “SHA256” option from the Menu:
Now click on the “Hash” button to start getting the Hash key for the Ubuntu ISO File:
Wait for the Digest to complete the process:
After the process is completed, the Digest Menu will return the Digest of the selected Hash Functions. In our case, we selected the SHA256 option, so the Digest will return the Hash Key of the SHA256 Hash Function:
Verify the Hash Value with the one from the Official Website. In our case, the Official Hash Value is “a435f6f393dda581172490eda9f683c32e495158a780b5a1de422ee77d98e909” and the Hash Generated by the Digest is “a435f6f393dda581172490eda9f683c32e495158a780b5a1de422ee77d98e909” which are both the same. This verifies the integrity and authenticity of our Ubuntu ISO File.
Method 3: Verify Ubuntu ISO Using the “sha256sum” Command
The Ubuntu ISO File can also be verified directly through the Terminal. The “sha256sum” command makes it easier to retrieve the Hash Value without having to use a third party. To use the “sha256sum” command, open the Terminal using the “ctrl+alt+t” shortcut key:
Navigate to the file directory using the “cd” Command. In our case, the file is in the Ubuntu Directory inside the Downloads Directory:
Once you are in the Ubuntu directory, use the “sha256sum” command along with the file name:
In our case, the file is the Ubuntu ISO File:
The Cursor will start blinking at the end ensuring that the command is retrieving the Hash Value of the Ubuntu ISO File. Wait for the process to complete:
Once the process is completed and the Hash Value of the Ubuntu ISO File is retrieved, the Hash Value will be displayed in the Terminal:
Once we retrieve the hash value with the “sha256sum” command, the official SHA256 Hash Value on the Ubuntu Website will be the same as the one retrieved with the command. In our case, the retrieved SHA256 Hash Value is “a435f6f393dda581172490eda9f683c32e495158a780b5a1de422ee77d98e909”, which is the same as “a435f6f393dda581172490eda9f683c32e495158a780b5a1de422ee77d98e909” from the Official Website. This is how easily you can verify the Ubuntu ISO Downloaded File with the “sha256sum” command.
Method 4: Verify Ubuntu ISO by Comparing the SHA256SUMS & SHA256SUMS.gpg Files
The Ubuntu ISO File can also be verified by comparing the “SHA256SUMS” and “SHA256SUMS.gpg” Files. Before comparing both Files, Import the GPG Keys from the Official Ubuntu Website using the “gpg” Command:
The Public Key once imported will be highlighted in the Terminal:
In case you want to verify the imported Keys, use the “gpg” command:
The Public Keys will be Listed:
Once added, download the SHA256SUMS and SHA256SUMS.gpg from the official Ubuntu Repository. To download the SHA256SUMS file, use the “wget” command:
The Terminal will save and inform about the success of the saved file:
Now, download the SHA256SUMS.gpg file using the “wget” command again:
The Terminal will save and inform about the success of the SHA256SUMS.gpg file:
Now verify the checksum file signature using the “gpg” command:
If the Terminal Returns a “Good Signature” Message, it means the Ubuntu ISO Image was signed by the owner of the file. In our case, the Checksum File Signature is Good:
To verify the integrity of the file, compare the downloaded SHA256SUM file with the generated SHA256 checksum. To do this execute the following “sha256sum” command:
If the output in Terminal displays “OK” along with the ISO Image file, it means the ISO file matches the Checksum verifying the file Integrity. In our case, the Command outputs “OK”:
This is how you can compare the Files and verify the integrity and authenticity of the Ubuntu ISO File.
Conclusion
Ubuntu Offers the SHA-256 cryptography security algorithm to verify file integrity. SHA-256 or Secure Hash Algorithm 256-bit produces irreversible and unique Hashes of a File. For verifying the File Integrity, the Hashes of both the Files must match, and the Hashes match only in the case of the data or content inside both the Files Matches.
The Integrity of the Ubuntu ISO File can be verified through the Official Ubuntu Checksum, using the Digests Method, using the sha256sum command, or by Comparing the SHA256SUM and SHA256SUM.gpg Files. All the methods for verifying the Ubuntu Downloaded ISO File are discussed in this article.
Discover more from Ubuntu-Server.com
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.