What is Ubuntu?
Ubuntu is a free and open-source operating system. Its architecture is based on Debian and based on a Linux distribution that allows the execution of different machines worldwide driven by open-source software. It permits you to alter the code, allows distribution of programs and installation of multiple copies without paying any cost.
The first ubuntu version was released in October 2004. The current release of Ubuntu is 20.04 LTS (Focal Fossa). Every release of ubuntu consists of a version number that consists of the year and month of distribution and a development code name. For example, the current version was released in 2020 in the month of April named focal fossa. LTS stands for Long term support which means every LTS release is supported for five years.
This guide is for beginners who are at the initial level of ubuntu or have decided to switch their operating system to Ubuntu. It will help you to understand the environment of ubuntu and its usage. To enter into a new operating system it is not necessary to replace your current operating system and install a new one. You can go for a trial or execute it on a virtual machine.
Prerequisites
The current version of Ubuntu is installed on your device or execution via a virtual machine.
Get Started
Now, let’s start to explore ubuntu from scratch.
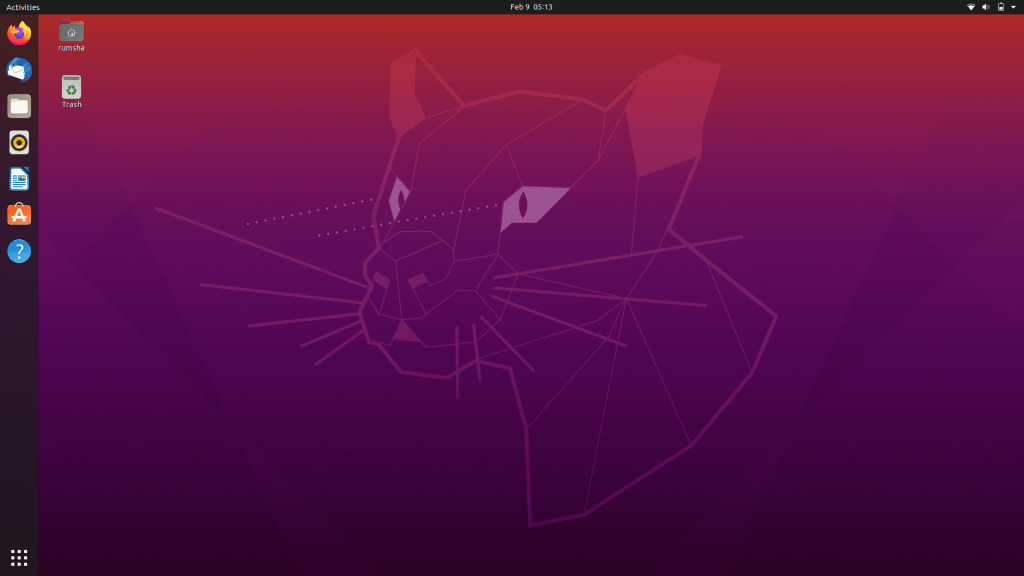
This is the main desktop screen of ubuntu when you first log in.
By default, Ubuntu uses the GNOME shell Desktop which is a graphical display referring to the GNOME environment. It is one of the GNU projects providing free software worldwide.
The GNOME desktop
Left Panel
On the left side of the screen, you can see a quick launch bar. It consists of default applications and shortcuts to applications.
Top Bar
Starting from the left you can see activities, date, and time in the middle proceeding right to network settings and battery of the device.
Navigating the top bar
You can easily set the date and time from the top bar.
You can connect to the internet by clicking on the right of the top bar.
You can also view system information and change settings as shown below:
Activities
The activities option shows the overview of all your open windows.
App drawer
The App drawer is present at the bottom of the quick launch bar that demonstrates all the installed applications in the form of a grid.
Search bar
The search bar is located at the top of the activities overview. You can easily find files, folders, and applications using the search bar.
Workspaces
Workspace is located on the right side of the overview screen. By default, there are two workspaces placed vertically. New one’s pop-ups automatically as per need.
Browsing web
You can easily browse the internet using Mozilla firefox. It is pre-installed in every release of Ubuntu.
Listening music
You can listen to music by using Rhythmbox which is the default media application in ubuntu. You can easily generate playlists and organize different audio files.
Watching video
You can play videos using the default GNOME video player for ubuntu. Besides this, it also offers VLC and Kodi that can be easily installed via the command-line interface.
Managing Photos
Ubuntu allows you to organize, view, and edit your images by installing packages from the repository. Such as
- Image viewer allows you to view images in the folder
- Shotwell is a personal photo manager for organizing images on the GNOME desktop.
Creating documents
Ubuntu comes with LibreOffice.It is open-source and free and provides the same functionality as Microsoft office.
Installing software
You can easily various software on ubuntu such as skype, Minecraft, dropbox, steam, Nvidia drivers, Spotify, and many more. You can either use GUI or command-line interface to install this software.
Command-line interface
To open the command line interface either write terminal, command, or shell in the search bar or press Ctrl-Alt-T.
Double click on the terminal to invoke the command-line interface. You will see a screen as given below:
Basic commands
Here are some basic commands of Ubuntu that you should know at the beginners level:
ls command
ls command shows the content of your current directory.
pwd command
pwd command shows the path of the current directory.
cd command
cd command moves you directly to the home folder.
Free
It shows the free memory left in your system.
Sudo -i
Sudo stands for Super user do. It has more privileges than a normal ubuntu user.
Clear
Clear command is used to clear your terminal.
Conclusion
This guide is very beneficial for beginners to understand the desktop environment and some basic commands of ubuntu. Now you can easily use ubuntu on your systems. This is just the overview of ubuntu to know more and understand ubuntu you can visit the official website of ubuntu.
Karim Buzdar holds a degree in telecommunication engineering and holds several sysadmin certifications including CCNA RS, SCP, and ACE. As an IT engineer and technical author, he writes for various websites.
Discover more from Ubuntu-Server.com
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.