One of the most frustrating problems Ubuntu 22.04 users may encounter is suddenly losing audio output – those soothing sounds from music or video playback abruptly disappearing. Troubleshooting sound problems on Ubuntu can seem daunting, but this guide aims to make the process straightforward for users of all skill levels. Whether you are faced with absolutely no audio or distorted output, this article will walk you through methodical steps to diagnose the underlying cause and restore seamless sound to your Ubuntu system. With the right knowledge and a systematic approach, you can banish audio gremlins and regain the rich listening experience that Ubuntu offers. The instructions provided here should equip any user, regardless of experience level, with the ability to troubleshoot any sound issues that may arise and get their Ubuntu audio back on track.
Read: How to fix Bluetooth connection issues on Ubuntu 22.04
Audio peripherals not recognized
On occasions, particularly during transitions from a prior version to an advanced LTS iteration such as Ubuntu 22.04, the identification of audio peripherals might encounter challenges. Presented below is an illustration of the typical expectations in such circumstances:
For output devices:
Ubuntu sound not working – standard use case
For intput devices:
Ubuntu no sound issue – standard use case
Under such circumstances, the underlying cause could potentially stem from a permission conflict within the PulseAudio configuration file. To address this, consider executing the provided commands below :
killall pulseaudio; rm -r ~/.config/pulse/*
Read: How to view your sound card information using the terminal in Ubuntu 18.04
Choosing the correct audio device
Multiple audio devices may be installed on a Linux computer, but not all of them are configured to output sound. To ensure the correct device is selected for audio output, follow these steps:
- a- Open the Activities overview and search for ‘Sound’
- b- Click on the Sound icon to open the audio settings panel
To configure the correct audio output device:
- 1. In the Sound settings panel, go to the Output Devices section.
- 2. Select one of the available audio devices from the list.
- 3. Adjust the configuration settings for that device as needed.
- 4. Test audio playback to see if sound outputs properly from that device.
- 5. If it does not work, select a different audio device from the list and repeat steps 3-4, modifying its settings and testing playback.
- 6. Repeat this process of selecting, configuring, and testing different audio devices until you find the one that successfully outputs sound as expected.
- 7. Once the correct audio output device is found, leave it selected as the default device.
Read: How to manage sound on Ubuntu 18.04
Muted audio?
It may seem odd, but sound being muted is a simple possibility worth checking. To rule it out as the issue:
- Look for a mute icon in the system menu bar. This will indicate if sound is silenced.
- Also verify the volume slider is not set extremely low or at minimum level, which would make audio inaudible.
- Checking the volume controls and mute status only takes a moment, and can identify if sound output is disabled before trying other troubleshooting steps.
Sound not working in Ubuntu 22.04 – standard use case
Make sure sound is not muted and volume is turned up as the first troubleshooting item. Resolving a simple mute or volume change could fix the lack of audio quickly.
Here are some additional troubleshooting steps to check for muted sound:
- Press any mute keys or switches on your computer’s keyboard, if present. Toggling these can unmute the sound if accidentally hit.
- Look for mute or volume controls in the media applications you are trying to play audio from. It’s possible you inadvertently muted sound within the app itself. Unmute and check volume in the application.
Suppose for instance you have Firefox active and a YouTube video is playing. In the event that the indicated setting is deactivated , the audio output of the video will remain inaudible.
Go to the Activities overview and input ‘Sound’. Proceed to access the Sound panel by selecting it.
Read: How to speed up Linux
Within the panel, navigate to the Volume Levels section and ensure that the sound level is neither set to a low value nor entirely muted (see Firefox app below):
As mentioned above, system-wide mute status and volume override app controls, so verify those are not disabled first. But also check for muted sound options within the specific media apps you’re using.
Sound card recognition
If the necessary audio drivers are missing, the sound card might encounter difficulties in proper detection. In such scenarios, a manual installation of the drivers becomes imperative. However, the approach may vary based on the specific sound card type. To ascertain the precise sound card type, you must execute the ‘lspci’ command.
Access the terminal and invoke the ‘lspci’ command while operating as the root user:
sudo lspci
Verify whether an audio device or controller is visible in the display. Should this be the case, make a record of the brand and model identification of the associated sound card. It’s important to bear in mind that the command:
lspci -v
Will offer additional comprehensive insights about the listed controllers.
Having obtained the details regarding your sound card, proceed to explore the manufacturer’s website. Ascertain whether they offer compatible drivers tailored for your system. Additionally, you might consider seeking assistance from relevant support forums to gather more insights.
For more details about the listed controllers, you might want to visit our article here.
Installation of Pavucontrol
PulseAudio lacks individual stream control, but Pavucontrol enables more precise audio device tuning. Installing Pavucontrol allows separate headphone and speaker adjustment that PulseAudio does not provide.
To install Pavucontrol, run the command:
sudo apt-get install pavucontrol
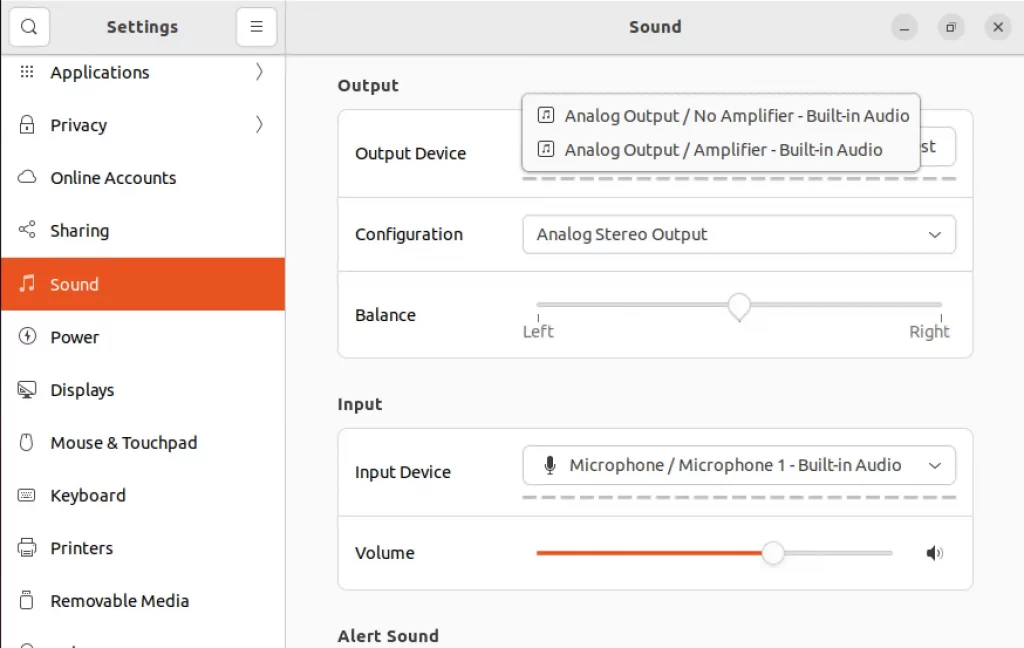
Next, execute the ‘pavucontrol’ command as shown below on the terminal. Within the Output Devices section, verify that your default speakers are selected:
Within the configuration tab, configure the profile to “Analog Stereo Output”:
Configuring Speaker Preferences
If your system possesses external speakers, it’s imperative to verify their operational status. Make sure the volume is neither set to its lowest level nor muted. Additionally, confirm the appropriate insertion of your speaker cable into the designated output audio socket (usually light green) on your computer. This precaution is essential to prevent potential scenarios where the audio cable is mistakenly attached to an incorrect port or remains loose altogether.
While seemingly simple, it’s worthwhile to thoroughly investigate this aspect: ensure that the audio cable is correctly inserted into the appropriate input socket of your speaker, considering that these speakers could possess multiple input sockets.
For those utilizing Bluetooth devices, it’s equally crucial to verify proper pairing.
Alsamixer
Though it might appear improbable, a situation could arise where all audio volume controls are maximized, yet no sound is audible. This potential anomaly might stem from the mixer control settings. To ascertain if this scenario applies, you should execute the ‘alsamixer’ command within your terminal, as outlined below:
alsamixer
This action will prompt the display of the following screen:
In the upper portion, you will locate the particulars concerning your sound card. In the central segment, the existing levels configuration is visible. Pressing the F6 key facilitates the selection of the desired sound card.
As depicted above, the Headphone bar had been muted, even though the Master bar was already at its maximum level. Should you encounter a similar setting, this could elucidate the underlying audio concern. To address this, employ the left/right arrow keys to highlight and select the headphones tab. Then, utilize the up/down arrow keys to elevate or reduce the volume. Conclude the interaction by pressing the ESC key to exit the interface.
Read: Best music players for Linux
You might have observed that “MM” is displayed beneath the volume bar when a mixer control is muted. To reverse this, press the “m” key, which will transform “MM” into “OO”.
Additionally, you have the option to adjust the volume using the following terminal commands:
amixer set Master 50%
For more info about the amixer command, execute :
amixer
The next section outlines the procedure for resetting or reloading ALSA, particularly when misconfiguration or unidentifiable issues arise.
Should the sound problem persist, consider reloading ALSA by executing the following command with elevated privileges:
sudo alsa force-reload
Reloading Pulseaudio and Alsamixer
Within this section, you’ll gain insights into restarting or reinstalling Alsa and PulseAudio if the previously mentioned solutions prove ineffective.
To initiate this process, run the subsequent commands within your terminal:
sudo apt-get remove –purge alsa-base pulseaudio
sudo apt-get install alsa-base pulseaudio
Ultimately, proceed to reboot your computer and reload Alsa as described in the previous section. Following these steps, you should be all set.
Fast Dispatcher Interference
The “Fast Dispatcher” function enables your system to transform text into speech. Occasionally, this feature clashes with other audio settings. If you find this feature unnecessary, consider deactivating it, which could potentially resolve your audio issues.
To proceed, open the terminal and modify the voice dialer file using this command:
sudo gedit /etc/default/speech-dispatcher
Within the file, alter the line from RUN=yes to RUN=no. Following this, reboot your system and verify whether your issue has been rectified.
The post How to troubleshoot sound issues in Ubuntu 22.04 appeared first on net2.
Discover more from Ubuntu-Server.com
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.