Ubuntu is a Debian-based open-source Linux distro released for Desktops, Severs, and IOT machines. Ubuntu OS has many advantages, such as being free to use, lightweight, secure, and fast. Additionally, Ubuntu needs fewer resources to work, meaning it can run on PCs with low specifications.
Ubuntu keeps on pushing updates every then and now, it releases standard updates every six months and LTS updates every two years. Thus, it is always recommended to keep your Ubuntu up to date to improve the system’s security.
Before updating Ubuntu, you must check its current version. Knowing the Ubuntu version lets you check whether a certain application is compatible with the current version and it also helps in troubleshooting compatibility issues with applications or software updates.
This guide will teach you:
How to Check Ubuntu Version
You can check the Ubuntu version using:
How to Check Ubuntu Version Using Terminal
These are the commands to check the Ubuntu version:
- lsb_release -a Command
- cat /etc/issue Command
- hostnamectl Command
- cat /etc/lsb-release Command
- cat /etc/os-release Command
- cat /proc/version Command
- uname -a Command
- cat /etc/*ease Command
- Screenfetch Tool
- Neofetch Tool
Method 1: lsb_release -a Command
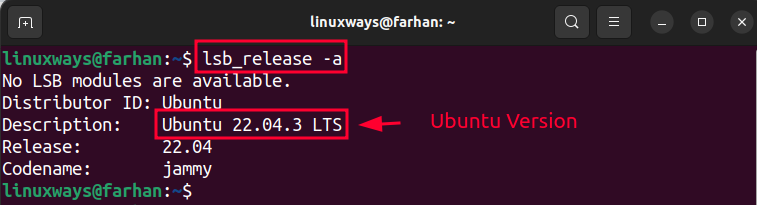
The lsb_release command gets the available LSB modules on Ubuntu. However, when the -a flag is added to that command, it displays complete details about the Ubuntu version.
To check the Ubuntu version, execute the given command:
The Ubuntu version can be seen in the Description and Release line.
To check only the Ubuntu version description, add the -d switch along with the lsb_release command:
Method 2: cat /etc/issue Command
The Ubuntu version is also stored in the issue file, which is placed within the etc directory. To retrieve the Ubuntu version information from this file, you can use the cat command followed by the /etc/issue location:
To get a more neat Ubuntu version, execute the cat /etc/issue.net command:
Method 3: hostnamectl Command
The hostnamectl command displays the host details including version, hostname, architecture, etc. Besides that, you will also get information about your current Ubuntu version using the hostnamectl command, as given below:
The Ubuntu version can be seen in front of the Operating System section.
Method 4: cat /etc/lsb-release Command
The Ubuntu version information is also available in the lsb-release file, which includes the Ubuntu version number and a description of Ubuntu distribution. Simply execute the cat /etc/lsb-release command in the terminal to check the Ubuntu version:
The Ubuntu version can be seen in front of DISTRIB_RELEASE and DISTRI_DESCRIPTION.
Method 5: cat /etc/os-release Command
The os-release is another system-related file placed in the /etc directory, which includes your system-related information including the Ubuntu version. To open this file, simply use the cat command followed by the /etc/os-release location to check the Ubuntu version:
Method 6: cat /proc/version Command
The Ubuntu version details are also stored in the version file placed within the proc folder on the system. To get the information stored in the version file, simply use the cat command along with the /proc/version path to check the Ubuntu version:
Method 7: uname -a Command
The uname command gets the name of the current operating system and also displays the kernel version. The uname command displays the Ubuntu version when used with the -a flag. To check the Ubuntu version, simply, run the uname -a command in the Terminal:
Method 8: cat /etc/*ease Command
The ease file in the etc directory also contains the Ubuntu information in detail including the version number. To access the ease file, use the cat command and place the /etc/*ease alongside it:
Method 9: Screenfetch Tool
Another way of displaying the Ubuntu version is using the Screenfetch tool, a command line tool that displays the full system details alongside the Ubuntu version. To use this tool for checking the Ubuntu version, follow the below-given steps:
Step 1: Install Screenfetch on Ubuntu
Screenfetch is not a built-in Ubuntu tool, you have to install it manually from the following command to check the Ubuntu version:
Step 2: Check the Ubuntu Version
Once the installation is completed, run the screenfetch command in the Terminal to check the Ubuntu version:
Method 10: Neofetch Tool
Like Screenfetch, neofetch is another tool that displays the Ubuntu version. Alongside full system details, it also displays the color palette. You can use the following steps to install the Neofetch tool for checking the Ubuntu version:
Step 1: Install the Neofetch on Ubuntu
You can install the Neofetch application on Ubuntu from the apt repository with the following command:
Type Y and press Enter to proceed with the installation process.
Step 2: Check Ubuntu Version
After completing the Neofetch installation, execute the neofetch command to get the Ubuntu version in Terminal:
How to Check Ubuntu Version Using GUI (Graphical User Interface)?
If you are new to the Ubuntu operating system then CLI might be difficult for you to understand. Check the step-by-step instructions to get the Ubuntu version using GUI.
Step 1: Launch Settings
Click on the top-right panel and select Settings:
Step 2: Check Ubuntu Version
Move to the About tab and look for the OS Name section to check the Ubuntu version:
Conclusion
Checking the Ubuntu version helps you update the version later on to improve your system performance and security. You can use both Terminal and GUI to check the Ubuntu version. In the terminal, you can check the Ubuntu version using commands like hostnamectl, cat, and lsb_release. and. You can also install command line utilities like Screenfetch, or Neofetch to check the Ubuntu version. The steps to check the Ubuntu version from the GUI are simple and the version can be figured out from the About tab in the Settings. It depends on your choice whether to go with Terminal and GUI, in all cases, you will get the information about your Ubuntu version.
Discover more from Ubuntu-Server.com
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.